What is a Switching Power Supply and How Does It Work?
The concept of a Switching Power Supply is fundamental in modern electronics. According to a report by MarketandResearch.biz, the global market for Switching Power Supplies is expected to reach $50 billion by 2025. This growth reflects their importance in various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial systems.
Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in energy efficiency, states, “Switching Power Supplies are integral to achieving optimal performance in electronic devices.” Her statement highlights the critical role these systems play in efficiency. Switching Power Supplies convert electrical power with minimal energy loss.
Despite their advantages, some challenges exist. Not all designs maximize energy efficiency, which can lead to increased costs. Industry leaders must continually innovate. Balancing performance and energy efficiency is essential. As the market evolves, the quest for better designs continues.
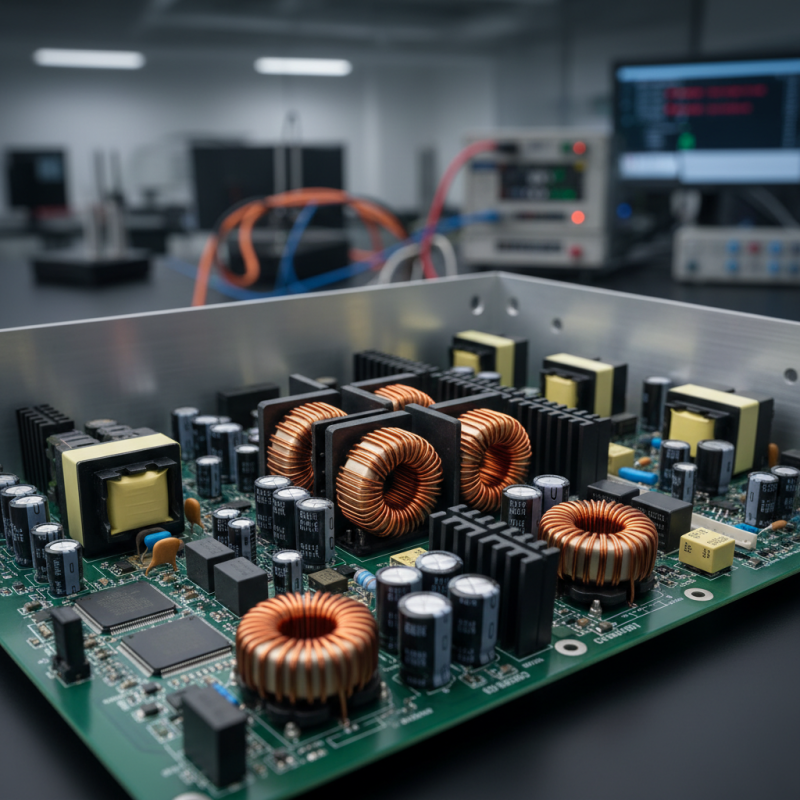
What is a Switching Power Supply?
A switching power supply is an essential component in modern electronics. Unlike traditional linear power supplies, they use switching regulators to convert electrical power more efficiently. This method significantly reduces energy loss, making them highly sought after in various devices. Reports indicate that switching power supplies can reach efficiency levels above 90%. This is particularly important for consumer electronics and industrial applications.
The fundamental principle behind a switching power supply involves converting high voltage DC into low voltage DC using a high-frequency switching technique. The high frequency allows for smaller components, reducing the overall size of the power supply. However, achieving such efficiency is not without challenges. Designers must manage issues like electromagnetic interference (EMI) and heat dissipation. Proper layout and shielding are critical to mitigate these problems.
Despite their advantages, not all switching power supplies are designed equally. Some may struggle with voltage regulation under varying load conditions. It's crucial to carefully select components and design approaches to enhance performance. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more refined designs. However, the industry must remain vigilant about the trade-offs between performance, size, and reliability. Understanding these factors is key to optimizing switching power supply designs.
The Key Components of a Switching Power Supply
A switching power supply is an essential device in modern electronics. It converts electrical energy from one voltage level to another efficiently. The key components that make this process effective include the transformer, rectifier, and control circuit.
The transformer is vital for voltage conversion. It steps up or steps down voltage levels as needed. This component ensures that devices receive the correct voltage to operate. The rectifier then converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This step is crucial, as most electronic devices require DC power to function properly. A poorly designed rectifier can lead to voltage spikes. Such spikes can damage connected components.
The control circuit manages the entire process. It regulates the output voltage by adjusting the switching frequency. This ensures stable performance even under varying load conditions. However, designing a control circuit can be challenging. Engineers must balance efficiency and responsiveness. Small errors can introduce noise, affecting overall performance. Proper debugging is essential to achieve optimal results.
How Switching Power Supplies Convert Power
Switching power supplies are essential in modern electronics. They efficiently convert electrical power from one form to another. This conversion process involves several stages that optimize performance and stability.
At the heart of a switching power supply is the oscillator. It rapidly turns the input voltage on and off, creating a pulsed signal. This signal is then transformed by an inductor or transformer. A rectifier is involved to convert the AC signal back into DC. Capacitors smooth out the fluctuations, providing a steady output.
Efficiency can be high, often above 85%. However, it’s important to consider potential heat generation and electromagnetic interference. Some designs may struggle with noise. Designers often need to balance efficiency with these issues. This reflection can lead to improvements in future designs, making power supplies even better.
Efficiency of Switching Power Supplies at Different Loads
This bar chart illustrates the efficiency of switching power supplies at various load levels. As shown, the efficiency tends to increase as the load increases, reaching a peak around 50-75% load, before slightly decreasing at full load. This behavior is typical for many power supply designs, emphasizing the importance of operating within optimal load conditions for maximum efficiency.
Advantages of Using Switching Power Supplies
Switching power supplies are popular in many devices today. They convert electrical power efficiently. These supplies feature a high-frequency switching mechanism. This design leads to several advantages.
The first advantage is their compact size. Unlike traditional power supplies, switching models are smaller and lighter. This makes them ideal for portable devices. They also generate less heat. This helps prolong the lifespan of electronic components.
Tips: When choosing a switching power supply, consider its efficiency rating. A higher rating means less waste. Also, think about the load requirements of your devices. You need the right match for optimal performance.
Another benefit is voltage regulation. Switching power supplies maintain a steady output voltage. This is crucial for sensitive electronics. Any fluctuations can cause damage. They also have good load transient response.
Tips: Always check the reviews before purchasing. Users often share insights about real-life performance. Look for warnings about overheating or noise. This feedback can be invaluable.
Common Applications of Switching Power Supplies
Switching power supplies are widely used in many devices. They efficiently convert electrical power from one voltage level to another. Common applications include computers, televisions, and industrial machines. In these devices, switching power supplies help save energy and reduce heat.
In consumer electronics, switching power supplies are essential. They can be found in laptops and mobile chargers. These supplies often take up less space compared to linear power supplies. This compact design is crucial in today’s portable gadgets. However, the noise generated by these supplies can affect sensitive equipment.
In industrial settings, switching power supplies power heavy machinery. They offer reliable performance under variable loads. Many factories rely on these supplies for automation processes. Nonetheless, improper selection can lead to inefficiencies and higher costs. It’s vital to match power supply specifications to the application. This aspect is often overlooked, so careful planning is necessary.

